 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)


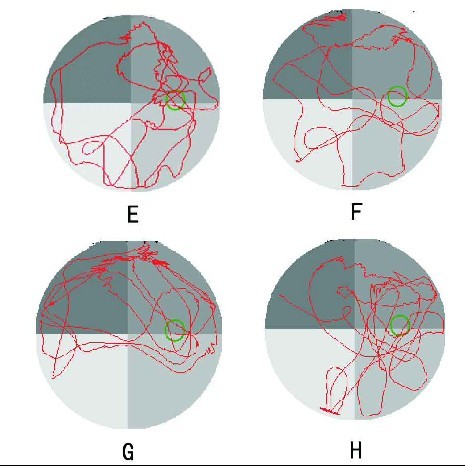
Effects of quercetin on the learning and memory ability of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
HUANG Jing-Jing, LIU Xuan, WANG Xing-Qi, YANG Li-Hua, QI Da-Shi, YAO Rui-Qin
Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics ›› 2012, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (06) : 454-457.
 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)
 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)
Effects of quercetin on the learning and memory ability of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
Quercetin / Hypoxia-ischemia / White matter damage / Morris water maze / Open-field test / Neonatal rats