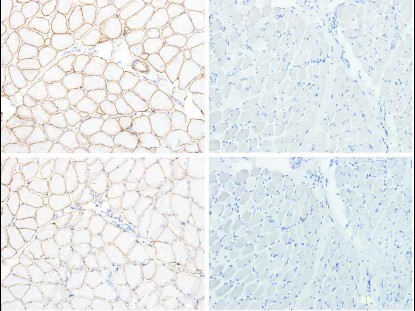
OBJECTIVE: To study the clinical and pathological features of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), with the aim of increasing the possibility of early diagnosis. METHODS: The clinical data of 50 children who were definitely diagnosed with DMD, based on clinical manifestations and the results of skeletal muscle biopsies and monoclonal antibody immunohistochemical staining, was reviewed. RESULTS: The children showed similar clinical manifestations, including running slowly in the toddler period, muscle weakness when climbing stairs and standing up followed by squatting down and walking abnormalities a predominant increase in serum creatine kinase level increased dominantly, and myopathic lesions seen on electromyography. Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed similar pathological presentations in all 50 children, including differentsized muscle fibers with rounding, degeneration and necrosis in various degrees, and proliferation of connective tissues. There was some inflammatory cell infiltration in muscle fibers and interstitial tissues. Dystrophin expression was completely absent at the sarcolemma in all 50 children, and sarcoglycan-α,-β, -γ,-δ expression was reduced to various degrees in 33 of them. CONCLUSIONS: For children with the clinical manifestations mentioned above, skeletal muscle biopsies and monoclonal antibody immunohistochemical staining are recommended as these examinations contribute to a definite diagnosis of DMD by demonstrating dystrophin deficiency at the sarcolemma.
Key words
Duchenne muscular dystrophy /
Skeletal muscle biopsy /
Creatine kinase /
Immunohistochemistry staining /
Dystrophin /
Child
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.content}}
References
[1]胡静.骨骼肌疾病临床病理诊断[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:1-274.
[2]Cohn RD, Campbell KP. Molecular basis of muscular dystrophies[J]. Muscle Nerve, 2000, 23(10): 1456-1471.
[3]Kunkel LM, Monaco AP, Middlesworth W, Ochs HD, Latt SA. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1985, 82(14): 4778-4782.
[4]申本昌, 张成, 陈松林,孙筱放,李少英,姚晓黎,等.非缺失/重复型Duchenne肌营养不良症患者的致病点突变分析[J].中华医学遗传学杂志, 2006, 23(4) : 392-396.
[5]Ray PN, Belfall B, Duff C, Logan C, Kean V, Thompson MW, et al. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X; 21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Nature, 1985, 318 (6047): 672-675.
[6]胡静,袁军辉,李娜,赵哲,沈宏锐,梅丽,刘彦. dysferlinopathy患者八例临床及分子病理学特点[J].中华神经科杂志, 2007, 40(12): 807-811.
[7]Petrof BJ. Molecular pathophysiology of myofiber injury in deficiencies of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex[J]. Am J Phys Med Rehabil, 2002, 81(11 Suppl): S162-S174.
[8]Kakulas BA. The differential diagnosis of the human dystrophinopathies and related disorders[J]. Curr Opin Neurol, 1996, 9(5): 380-388.
[9]Fairclough RJ, Bareja A, Davies KE. Progress in therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy [J]. Exp Physiol, 2011, 96(11): 1101-1113.
 PDF(1412 KB)
PDF(1412 KB)


 PDF(1412 KB)
PDF(1412 KB)
 PDF(1412 KB)
PDF(1412 KB)