 PDF(1782 KB)
PDF(1782 KB)


A modified culture method for astrocytes from rat cortical tissue in vitro
GUO Hui, MAO Meng, YU Dan, ZHOU Hui, TONG Yu
Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics ›› 2014, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (12) : 1271-1274.
 PDF(1782 KB)
PDF(1782 KB)
 PDF(1782 KB)
PDF(1782 KB)
A modified culture method for astrocytes from rat cortical tissue in vitro
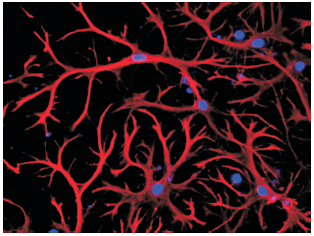
Objective To evaluate the efficiency of a modified culture method for rat cerebral cortical astrocytes in vitro. Methods The astrocytes derived from the cerebral cortex of 3-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats were first purified as described previously, then the cells were replanted at a low density. The culture flask was changed after 1 hour and substratum was replaced after 24 hours. Cells were syncretized to a monolayer, followed by cell passage. After three passages the cells were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal serum for a long period. The derivation of the cells was identified by immunofluorescent staining with anti-GFAP polyclonal antibodies. Results A variety of morphologically distinct astrocytes with many long processes and small cell bodies were obtained. Finally an astrocytic network occurred through cellular process connections. The immunofluorescent staining demonstrated the percentage of GFAP-positive cells was above 98%. Conclusions The modified culture method for astrocytes from rat cerebral tissue is reliable, with a high purity. The cultured astrocytes have a similar morphological development to those in vivo.
Astrocyte / Cell culture / Glial fibrillary acidic protein / Rats