 PDF(2790 KB)
PDF(2790 KB)


 PDF(2790 KB)
PDF(2790 KB)
 PDF(2790 KB)
PDF(2790 KB)
胰岛素样生长因子-1对缺氧缺血性脑损伤大鼠远期焦虑行为的影响
Effect of IGF-1 on long-term anxiety-like behavior in rats after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
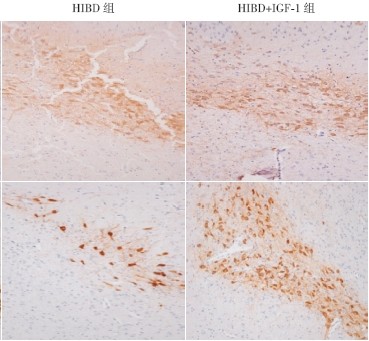
目的 了解围产期缺氧缺血性脑损伤(HIBD)恢复期大鼠焦虑行为的变化,并通过胰岛素样生长因子-1(IGF-1)的干预来探讨IGF-1 对HIBD 大鼠远期焦虑行为的影响和相关机制。方法 将90 只新生7日龄(P7)大鼠随机分为正常对照组、HIBD 组和HIBD+IGF-1 组,每组30 只。Rice 法制作新生大鼠HIBD 模型,HIBD+IGF-1 组于缺氧缺血(HI)后即刻腹腔注射IGF-1(0.2 mg/kg),其余两组腹腔注射等量的生理盐水。各组于P21 和P28 时采用高架十字迷宫检测动物的焦虑行为,并于P14、P21、P28 时采用免疫组织化学方法检测中脑黑质酪氨酸羟化酶(TH)的表达。结果 P21、P28 时,HIBD 组和HIBD+IGF-1 组的开放臂停留时间和开放臂停留时间比率均明显低于正常对照组(均P<0.05),但HIBD 组与HIBD+IGF-1 组之间差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05);这两个时间点开放臂进入次数比率在3 组间的差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。P14 时各组的TH免疫染色阳性面积百分比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);P21 和P28 时,HIBD 组和HIBD+IGF-1 组的TH 免疫染色阳性面积百分比均明显低于正常对照组(均P<0.05),但HIBD 组与HIBD+IGF-1 组之间差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。结论 围产期HI 损伤可使大鼠青春期焦虑行为发生改变,其机制可能与脑黑质TH 表达的减少相关;初生时给予IGF-1 干预对大鼠HIBD 远期焦虑行为的异常不产生作用,且IGF-1 不影响脑黑质TH 的表达,大鼠青春期焦虑样行为的改变可能不受IGF-1 调控。
Objective To observe the changes in anxiety-like behavior among rats in the recovery stage after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) during the perinatal period and to investigate the effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) on the long-term anxiety-like behavior and its action mechanism among rats with HIBD. Methods Ninety neonatal rats (7 days old) were randomly and equally divided into normal control, HIBD, and HIBD+IGF-1 groups. A neonatal rat model of HIBD was established by Rice method in the HIBD and HIBD+IGF-1 groups. The rats in the HIBD+IGF-1 group were intraperitoneally injected with IGF-1 (0.2 mg/kg) immediately after HIBD, and the other two groups were intraperitoneally injected with an equal volume of normal saline. The anxiety-like behavior was evaluated by elevated plus-maze test on postnatal days 21 and 28. The expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in the substantia nigra was measured by immunohistochemistry on postnatal days 14, 21, and 28. Results On postnatal days 21 and 28, the open-arm time (OAT) and percentage of OAT for the HIBD and HIBD+IGF-1 groups were significantly lower than those for the normal control group (P<0.05), but there were no significant differences between the HIBD and HIBD+IGF-1 groups (P>0.05); the percentage of open arm entry showed no significant difference between the three groups (P>0.05). On postnatal day 14, there were no significant differences in percentage of TH immunostaining-positive area between the three groups (P>0.05). On postnatal days 21 and 28, the HIBD and HIBD+IGF-1 groups had significantly lower percentages of TH immunostaining-positive area than the normal control group (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between the HIBD and HIBD+IGF-1 groups (P>0.05). Conclusions HIBD in the perinatal period may cause the changes in anxiety-like behavior in adolescent rats, which may be related to decreased expression of TH in the substantia nigra. Neonatally given IGF-1 cannot improve the long-term anxiety-like behavior in rats after HIBD, and it does not affect TH expression in the substantia nigra. IGF-1 may not regulate the changes in longterm anxiety-like behavior in adolescent rats.
缺氧缺血性脑损伤 / 远期 / 焦虑行为 / 酪氨酸羟化酶 / 胰岛素样生长因子-1 / 新生大鼠
Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage / Long-term / Anxiety-like behavior / Tyrosine hydroxylase / Insulinlike growth factor 1 / Neonatal rats
湖南省科技厅科研课题(2008FJ3157)。