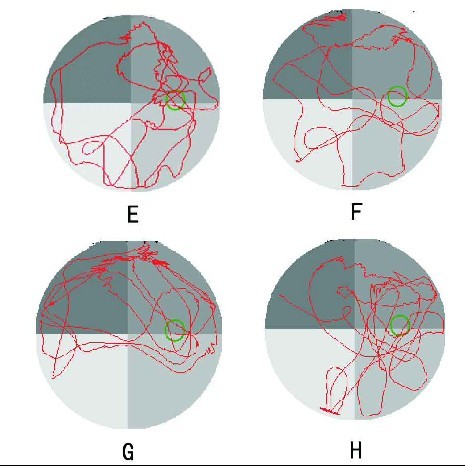
目的:研究槲皮素(QUE,黄酮类化合物) 对缺氧缺血性脑白质损伤新生大鼠学习记忆能力的影响。方法:生后3 d Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠60只,随机分成对照组、模型组和QUE处理组(20 mg/kg 和40 mg/kg),每组15只。模型组和QUE处理组行右侧颈总动脉结扎及缺氧处理以建立缺血缺氧性脑白质损伤模型。QUE处理组每日给药一次,连续6 周。第6周时分别用Morris水迷宫及开场试验评价其学习记忆能力和行为情感。结果:从训练的第2天开始,模型组逃避潜伏时间(EL)明显长于对照组(P<0.01), 20和40 mg/kg QUE处理组EL明显短于模型组(P<0.05)。模型组大鼠穿越原平台次数明显低于对照组(P<0.01)及两个QUE组(P<0.05)。开场试验显示,模型组大鼠后肢站立次数较对照组增加,中央区域驻留时间较对照组延长,QUE处理后大鼠后肢站立次数较模型组明显减少(P<0.05),中央区域驻留时间明显缩短(P<0.05)。结论:QUE可以明显改善缺血缺氧性脑白质损伤新生大鼠的学习记忆及行为情感障碍,对中枢神经系统脑白质损伤具有保护作用。
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To study the effects of quercetin, a flavonoid, on the learning and memory ability of 3-day-old neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain white matter damage (WMD). METHODS: Sixty 3-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, WMD model,and quercetin treatment groups (20 and 40 mg/kg). There were 15 rats in each group. Rats in the WMD model and the two quercetin treatment groups were subjected to right common carotid artery ligation followed by 2 hrs of exposure to 8% O2 to induce periventricular white matter injury. After the operation quercetin was administered daily in the two quercetin treatment groups for 6 weeks. Six weeks later, Morris water maze and open-field tests were carried out to test memory and learning ability as well as behavior and cognition. RESULTS: From the second day of training, escape latency in the Morris water maze test was more prolonged in the WMD model group than in the control group (P<0.01). The escape latency in the two quercetin treatment groups was shortened significantly compared with the WMD model group (P<0.05). The WMD model group crossed the original platform fewer times compared with the control and quercetin treatment groups (P<0.05). The open-field test indicated that the number of rearings increased and time spent in the centre was extended in the WMD model group compared with the control group. Compared with the WMD model group, the number of rearings was significantly reduced (P<0.05) and time spent in the centre was significantly shortened in the quercetin treatment groups (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: Quercetin treatment can improve memory and learning ability as well as cognitive ability in neonates with WMD, suggesting that quercetin protects against WMD resulting from hypoxia-ischemia.
关键词
槲皮素 /
缺血缺氧 /
脑白质损伤 /
Morris水迷宫 /
开场试验 /
新生大鼠
Key words
Quercetin /
Hypoxia-ischemia /
White matter damage /
Morris water maze /
Open-field test /
Neonatal rats
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.content}}
参考文献
[1]Sundrum R, Logan S, Wallace A, Spencer N. Cerebral palsy and socioeconomic status: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Arch Dis Child, 2005: 90(1): 15-18.
[2]Cai Z, Pang Y, Xiao F, Rhodes PG. Chronic ischemia preferentially causes white matter injury in the neonatal rat brain[J]. Brain Res, 2001, 898(1): 126-135.
[3]Kamaraj S, Vinodhkumar R, Anandakumar P, Jagan S, Ramakrishnan G, Devaki T. The effects of quercetin on antioxidant status and tumor markers in the lung and serum of mice treated with benzo(a)pyrene[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2007, 30(12): 2268-2273.
[4]Kumar A, Sehgal N, Kumar P, Padi SS, Naidu PS. Protective effect of quercetin against ICV colchicine-induced cognitive dysfunctions and oxidative damage in rats[J]. Phytother Res, 2008, 22(12): 1563-1569.
[5]Oz-elik B, Kartal M, Orhan I.Cytotoxicity, antiviral and antimicrobial activities of alkaloids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids[J]. Pharm Biol, 2011, 49(4): 396-402.
[6]程超,陆军,郑元林,刘文. 槲皮素对衰老小鼠学习记忆行为的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2004,24(11):1057-1059.
[7]王兴启,刘轩,杨丽华,于红丽,翟玥,刘静,等. 槲皮素保护少突胶质前体细胞缺氧低糖损伤的体外研究[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(3):338-341.
[8]Wang XQ, Yao RQ, Liu X, Huang JJ, Qi DS, Yang LH. Quercetin protects oligodendrocyte precursor cells from oxygen/glucose deprivation injury in vitro via the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2011, 86(3-4): 277-284.
[9]曾田,杨丽华,黄晶晶,戚大石,王兴启,刘轩,等. 缺血缺氧性脑损伤对新生3日龄幼鼠学习记忆及情感行为的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2010,20(23):3530-3538.
[10]Back SA, Luo NL, Borenstein NS, Levine JM, Volpe JJ, Kinney HC. Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal white matter injury[J]. J Neurosci, 2001, 21(4): 1302-1312.
[11]Pu F, Mishima K, Irie K, Motohashi K, Tanaka Y, Orito K, et al. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin and rutin on spatial memory impairment in an 8-arm radial maze task and neuronal death induced by repeated cerebral ischemia in rats[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2007, 104(4): 329-334.
[12]Liu J, Yu H, Ning X. Effect of quercetin on chronic enhancement of spatial learning and memory of mice[J]. Sci China C Life Sci, 2006, 49(6): 583-590.
[13]Lu J, Zheng YL, Luo L, Wu DM, Sun DX, Feng YJ. Quercetin reverses D-galactose induced neurotoxicity in mouse brain[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2006, 171(2): 251-260.
[14]Yao Y, Han DD, Zhang T, Yang Z. Quercetin improves cognitive deficits in rats with chronic cerebral ischemia and inhibits voltage-dependent sodium channels in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons[J]. Phytother Res, 2010, 24(1): 136-140.
[15]Ahmad A, Khan MM, Hoda MN, Raza SS, Khan MB, Javed H, et al. Quercetin protects against oxidative stress associated damages in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion[J]. Neurochem Res, 2011, 36(8): 1360-1371.
 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)


 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)
 PDF(1210 KB)
PDF(1210 KB)