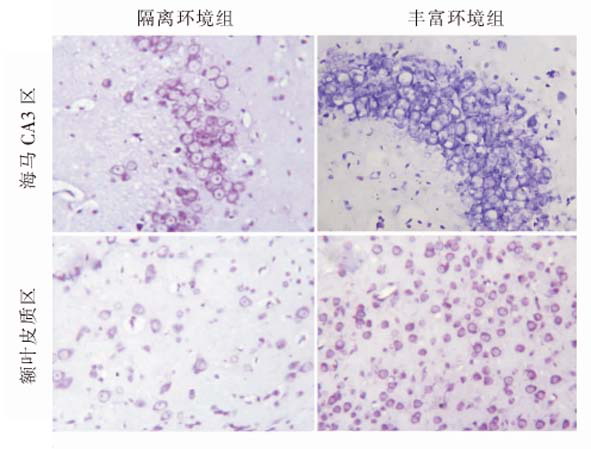
目的:通过研究早期环境对大鼠学习记忆能力及脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)及其受体—酪氨酸激酶受体B(TrkB)表达的影响,探讨早期环境对发育期大鼠脑发育的影响及可能调控机制。方法:45只新生Sprague-Dawlely(SD)大鼠随机分为丰富环境组、隔离环境组及对照组,每组15只。丰富环境组处于丰富环境中饲养,隔离环境组大鼠在单调环境下成长,对照组大鼠在普通环境中常规饲养。大鼠生后28~29 d采用“Y”臂迷宫试验检测学习记忆功能。海马CA3区与额叶皮质区神经元数量及BDNF、TrkB表达水平分别采用尼氏染色、免疫组织化学染色方法进行检测。结果:与隔离环境组及对照组相比,丰富环境组大鼠达到学会标准所需训练的次数减少(P<0.01),记忆保持百分率提高(P<0.01);与对照组相比,隔离环境组大鼠达到学会标准所需训练的次数增加(P<0.01),记忆保持百分率下降(P<0.01)。尼氏染色结果显示,3组间额叶皮质区及海马CA3区神经元数量以丰富环境组最高,对照组次之,隔离环境组最低(P<0.01);免疫组织化学染色结果显示,丰富环境组大鼠海马CA3区及额叶皮质区BDNF及TrKB表达水平高于对照组和隔离环境组(P<0.01),且隔离环境组BDNF及TrKB表达水平低于对照组(P<0.01)。结论:早期环境可通过影响海马与额叶BDNF及其受体TrkB表达,而影响发育期大鼠远期脑发育及脑功能。
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To study the effect of early environment on the learning-memory ability of rats and the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptor, tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB), and to explore the influence of early environment on development of rat brain in developing stage and possible regulation mechanisms. METHODS: Forty-five newborn Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into three groups (15 rats in each group): enriched environment group (EE group), isolated environment group (IE group) and normal control group (NC group). The pups were nurtured separately in their groups. The learning-memory abilities of the rats were measured by "Y"-arm maze test 28 to 29 days after birth. The number of neural cells and the expression of BDNF and TrkB in the hippocampal CA3 and frontal lobewere were detected by Nissl’s staining and immunohistochemistry respectively. RESULTS: The results of the "Y"-arm maze test showed that rats in the EE group needed less training times, and retained a higher percentage of memory than the other two groups (P<0.01). Rats in the IE group needed more training times, and retained a lower percentage of memory than the NC group (P<0.01). By Nissl’s staining, the numbers of neural cells in the hippocampal CA3 and frontal lobe were highest in the EE group followed by the NC group. They were lowest in the IE group (P<0.01). By immunohistochemistry, the expression of BDNF in the hippocampal CA3 and frontal lobe were highest in the EE group followed by the NC group. It was lowest in the IE group (P<0.01). Results were similar for expression of TrkB. CONCLUSIONS: Early environment can affect the long-term brain development and brain function of rats by influencing the expression of BDNF and its receptor TrkB in the hippocampus and frontal lobe.
关键词
早期环境 /
脑源性神经营养因子 /
酪氨酸激酶受体B /
脑发育 /
大鼠
Key words
Early environment /
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor /
Tyrosine kinase receptor B /
Brain development /
Rats
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.title}}
{{custom_sec.content}}
参考文献
[1]Will B, Galani R, Kelche C, Rosenzweig MR. Recovery from brain injury in animals:relative efficacy of environmental enrichment, physical exercise or formal training (1990-2002)[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2004, 72(3): 167-182.
[2]陆澄秋,钟乐,田英,颜崇淮,沈晓明.断乳前丰富环境对即刻早期基因Are的表达及长时记忆的影响[J].中国当代儿科杂志, 2008,10(2):179-182.
[3]Woodcock EA, Richardson R. Effects of multisensory environmental stimulation on contextual conditioning in the developing rat[J]. Neurobiol Learn Mem, 2000, 74(2): 89-104.
[4]Hui JJ, Zhang ZJ, Liu SS, Xi GJ, Zhang XR, Teng GJ, et al. Hippocampal neurochemistry is involved in the behavioural effects of neonatal maternal separation and their reversal by post-weaning environmental enrichment: a magnetic resonance study[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2011, 217(1): 122-127.
[5]Callaghan BL, Richardson R.Maternal separation results in early emergence of adult-like fear and extinction learning in infant rats[J]. Behav Neurosci, 2011, 125(1): 20-28.
[6]Morrison AP. A cognitive behavioural perspective on the relationship between childhood trauma and psychosis[J]. Epidemiol Psichiatr Soc, 2009, 18(4): 294-298.
[7]刘玲,陈燕惠,陈达光.早期干预对宫内缺氧缺血大鼠脑电波及存活神经元数目的影响[J]. 中华妇幼临床医学杂志,2007,3(2):91-93.
[8]马良,陈燕惠,韦立新.早期丰富环境对大鼠远期行为发育及血清皮质酮的影响[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志,2011,13(7):586-589.
[9]Lee JH, Kim HJ, Kim JG, Ryu V, Kim BT, Kang DW, et al. Depressive behaviors and decreased expression of serotonin reuptake transporter in rats that experienced neonatal maternal separation[J]. Neurosci Res, 2007, 58(1): 32-39.
[10]章子贵,杜红燕,陆汉新,张维宁,吴馥梅.自然衰老过程中小鼠学习记忆行为变化的动态观察[J]. 中国老年学杂志,1995,15(6):354-356.
[11]Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:71-104.
[12]Cohen S, Greenberg ME. Communication between the synapse and the nucleus in neuronal development, plasticity, and disease[J]. AnnuRev Cell Dev Biol, 2008, 24: 183-209.
[13]Nagappan G, Lu B. Activity-dependent modulation of the BDNF receptor TrkB: mechanisms and implications[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2005, 28(9): 464-471.
[14]Yamada K, Mizuno M, Nabeshima T. Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory[J]. Life Sci, 2002, 70(7): 735-744.
[15]Martinowich K, Manji H, Lu B. New insights into BDNF function in depression and anxiety[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2007, 10(9): 1089-1093.
[16]Broersen LM.Attentional processes and learning and memory in rats: the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus compared[J]. Prog Brain Res, 2000, 126: 79-94.
[17]Howland JG, Wang YT. Synaptic plasticity in learning and memory: stress effects in the hippocampus[J]. Prog Brain Res, 2008, 169: 145-158.
 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)


 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)
 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)