 PDF(1363 KB)
PDF(1363 KB)


 PDF(1363 KB)
PDF(1363 KB)
 PDF(1363 KB)
PDF(1363 KB)
cbIC型甲基丙二酸血症基因型与临床表型及疗效的关系
Relationship of genotypes with clinical phenotypes and outcomes in children with cobalamin C type combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria
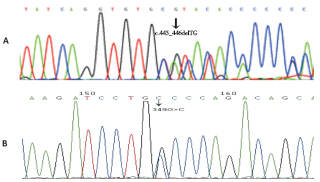
目的 分析cbIC型甲基丙二酸血症伴同型半胱氨酸血症(合并型MMA)基因突变情况、临床特点及治疗转归,探讨基因型与临床表型及疗效之间的关系。方法 回顾性分析16例经基因检测确诊为cbIC型MMA患儿的临床资料。按发病年龄分为早发型(≤1岁)及晚发型(> 1岁)。按临床表型分为轻型、中间型及重型。治疗方法为肌肉注射维生素B12(氰钴胺)/羟钴胺、口服甜菜碱、叶酸及左旋肉碱等。结果 早发型15例(重型11例、中间型4例),晚发型(轻型)1例。发现7种已经报道的突变及2种新发突变(c.445_446delTG和c.349G> C)。c.609G> A及c.658_660delAAG为最常见的突变(13/16,81%),二者导致的复合杂合突变为最常见(4/16,25%)的基因型,患者小头畸形及眼部问题表现突出且治疗后无缓解。晚发型这例患儿治疗后临床表型正常,早发型15例患儿表型越重、疗效越差。结论 我国cblC型MMA以早发型为主,存在热点突变c.609G > A和c.658_660delAAG;患儿临床表型与疗效相关。
Objective To analyze mutation types, clinical features, and treatment outcomes of cobalamin C (cblC) type combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria (MMA-HC) and to investigate the relationship of genotypes with clinical phenotypes and outcomes. Methods The clinical data of 16 Chinese children diagnosed with cblC type MMA-HC by gene analysis were retrospectively analyzed. According to the onset age, the patients were classified into early onset (≤1 year) and late onset (> 1 year). According to the clinical phenotype, the patients were classified into mild, moderate, and severe groups. All the patients were treated with vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) or hydroxocobalamin, betaine, folate, vitamin B6, and L-carnitine. Results Fifteen patients belonged to the early onset type, including 11 in the severe group and 4 in the moderate group. The remaining one belonged to the late onset type. Seven reported mutations and two novel mutations (c.445_446delTG and c.349G> c) were detected. The c.609G> A and c.658_660delAAG were the most common mutations detected in 13 (81%) out of 16 patients. The genotype caused by compound heterozygous mutations of these two alleles (c.609 G> A/c.658_660delAAG) was the most common in the patients, detected in 4 (25%) out of 16 patients. Patients with this genotype had severe microcephaly and eye diseases and these clinical manifestations were not improved after the treatment. The patient with late-onset cblC type MMA-HC had normal clinical phenotypes after treatment. In the 15 early onset patients, the more severe the clinical phenotype, the worse the treatment outcome. Conclusions The cblC type MMA-HC mainly manifests as early onset in China and c.609G > A and c.658_660delAAG are the most common mutations causing this disease. The clinical phenotypes are associated with the outcomes in children with cblC type MMA-HC.
甲基丙二酸血症 / 同型半胱氨酸血症 / 早发型 / 基因突变 / 转归 / 儿童
Methylmalonic aciduria / Homocystinuria / Early onset / Gene mutation / Outcome / Child