 PDF(2157 KB)
PDF(2157 KB)


eNOS和NADPH氧化酶在慢性缺氧条件下小鼠肺组织中表达关系的研究
吴西玲, 杜立中, 徐雪峰
中国当代儿科杂志 ›› 2015, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (9) : 1001-1006.
 PDF(2157 KB)
PDF(2157 KB)
 PDF(2157 KB)
PDF(2157 KB)
eNOS和NADPH氧化酶在慢性缺氧条件下小鼠肺组织中表达关系的研究
Relationship between expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and NADPH oxidase in lungs of mice exposed to chronic hypoxia
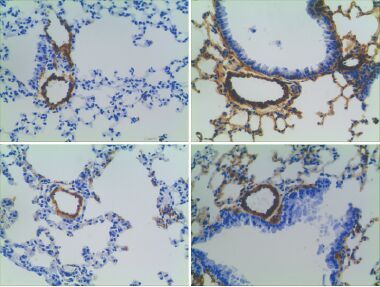
目的 探讨eNOS 和NADPH 氧化酶在慢性缺氧条件下小鼠肺组织中表达的关系。方法 将野生型及eNOS 基因敲除的C57BL/6 雄性小鼠各30 只随机分为常氧组、低氧7d组、低氧21d组、治疗7d组和治疗21d组,每种每组小鼠各6只。低氧和治疗组小鼠在10% 氧浓度条件下进行饲养,治疗组小鼠饮水中加入10 mmol/L 4-羟基-2, 2, 6, 6-四甲基哌啶(TEMPOL)进行干预。比较各组小鼠肺小动脉重塑(MT%)及右心室肥厚指标的变化;ELISA 法检测各组肺组织ROS 浓度的变化;RT-PCR 法检测各组肺组织NOX2、4 及eNOS 基因表达的变化。结果 野生型及基因敲除低氧组小鼠肺血管重塑及右心室肥厚指标较常氧组和治疗组均明显上升(P<0.05),而治疗组和常氧组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。野生型低氧及治疗组小鼠肺组织ROS浓度均低于常氧组(P<0.05),而低氧组和治疗组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。野生型低氧组小鼠eNOS、NOX2 和NOX4 的mRNA 表达较常氧组均显著上升(P<0.05),TEMPOL 干预可逆转上述指标的过度表达。基因敲除常氧组小鼠NOX2 和NOX4 mRNA 表达高于同组野生型小鼠(P<0.05);慢性缺氧后NOX4 mRNA表达较常氧组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),NOX2 mRNA 表达较常氧组显著下降(P<0.05);治疗组NOX2mRNA 表达较低氧组进一步下降,而NOX4 mRNA 表达较低氧组明显上升(P<0.05)。结论 eNOS 是低氧条件下NOX2、4 表达的重要调控因素,eNOS 和NOX 在低氧性肺血管重塑过程中可能有着重要的联系。
Objective To explore the relationship between the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and NADPH oxidase (NOX) in the lungs of mice treated by chronic hypoxic exposure.Methods Thirty male wild-type (WT) C57Bl/6 mice and thirty male eNOS-knockout (KO) C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into normoxic groups (exposed to normoxia for 7 days or 21 days), hypoxic groups (exposed to 10% oxygen for 7 days or 21 days), and treatment groups (exposed to 10% oxygen and orally administrated 10 mmol/L 4-hydroxy TEMPO in drinking water for 7 days or 21 days) (n=6 in each group). The remodeling of the small pulmonary arteries was evaluated by the percentage of media wall thickness (MT%). The weight ratio of right ventricle to left ventricle plus septum (RV/[LV+S]) was calculated to evaluate the hypertrophy of right ventricle. Real-time PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of NOX2, NOX4, and eNOS in mouse lungs. ELISA was used to determine the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mouse lungs.Results In WT mice and KO mice, the hypoxic groups had significantly increased pulmonary vascular remodeling and RV/[LV+S] compared with the normoxic and treatment groups (P<0.05), but there were no significant differences between the normoxic and treatment groups (P>0.05). In WT mice, the hypoxic and treatment groups had significantly lower ROS concentrations than the normoxic group (P<0.05), but there were no significant differences between the hypoxic and treatment groups (P>0.05). In WT mice, the mRNA expression of eNOS, NOX2, and NOX4 was significantly higher in the hypoxic group than in the normoxic group (P<0.05), and 4-hydroxy TEMPO reversed their over-expression. In the normoxic group, the KO mice had significantly higher NOX2 and NOX4 mRNA expression than the WT mice (P<0.05); in KO mice, the hypoxic group showed no significant changes in NOX4 mRNA expression (P>0.05), but had significantly reduced NOX2 mRNA expression (P<0.05), as compared with the normoxic group; the treatment group had reduced expression of NOX2 mRNA expression and increased NOX4 mRNA expression (P<0.05), as compared with the hypoxic group.Conclusions eNOS plays a key role in the regulation of expression of NOX2 and NOX4 in the lungs exposed to hypoxia. It suggests that NOX and eNOS may physically interact with one another in pulmonary vascular remodeling induced by chronic hypoxia.
内皮型一氧化氮合酶 / NADPH 氧化酶2 / NADPH 氧化酶4 / 4-羟基-2, 2, 6, 6-四甲基哌啶 / 反应性氧化物 / 小鼠
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase / NADPH oxidase 2 / NADPH oxidase 4 / 4-hydroxy TEMPO / Reactive oxygen species / Mice
浙江省教育厅课题(Y201017396)