 PDF(3162 KB)
PDF(3162 KB)


 PDF(3162 KB)
PDF(3162 KB)
 PDF(3162 KB)
PDF(3162 KB)
新生大鼠缺氧缺血脑损伤时脑组织STAT3信号通路的作用
Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage of neonatal rats
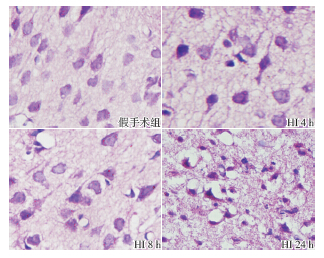
目的 研究信号转导和转录激活因子3(STAT3)信号通路在新生大鼠缺氧缺血脑损伤中的作用和机制。方法 80 只7 日龄Sprague-Dawley 大鼠随机分为缺氧缺血(HI) 组(n=40)和假手术组(n=40)。HI 组大鼠行右侧颈总动脉结扎随后缺氧(8% O2)处理2.5 h,假手术组仅分离右侧颈总动脉但不予结扎和缺氧处理。两组分别在HI 后4、6、8、12 和24 h 处死大鼠并收集脑组织。采用免疫组化和Westernblot 法检测STAT3、磷酸化STAT3 和血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)蛋白表达,TUNEL 染色法检测细胞凋亡。结果 HI 组和假手术组间STAT3 蛋白表达在各时间点差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);除24 h 外,其余时间点HI 组的磷酸化STAT3 蛋白表达均明显高于假手术组,6 h 达高峰(P<0.01)。各时间点HI 组VEGF 蛋白表达均明显高于假手术组,8 h 达高峰(P<0.05)。HI 组各时间点凋亡细胞数均高于假手术组,且随时间延长凋亡细胞数逐渐增加(P<0.01)。结论 新生大鼠HI 后STAT3 可能被磷酸化激活从而诱导VEGF 表达;STAT3通路激活可能参与了神经细胞的凋亡调节,推测该通路活化与神经细胞的凋亡抑制相关。
Objective To study the role and mechanisms of STAT3 signaling pathway in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) of neonatal rats. Methods Eighty 7-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into two groups: HI and sham-operated (n=40 each). The rats in the HI group were subjected to right carotid artery ligation and subsequent hypoxia exposure (8% O2) for 2.5 hours, and the rats in the sham-operated group underwent the right carotid artery dissection without subsequent ligation or hypoxia treatment. Brain tissue samples were collected at 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 hours after operation and hypoxic exposure. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot were used to detect the expression of STAT3, phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) proteins. TUNEL staining was used to detect apoptotic cells. Results No significant difference in STAT3 expression was observed at all time points between the HI and sham-operated groups (P>0.05). Compared with the sham-operated group, the expression of p-STAT3 protein in the HI group was significantly upregulated at 4, 6, 8, 12 hours after operation and hypoxic exposure, and peaked at 6 hours (P<0.01). The VEGF expression in the HI group was higher than that in the sham-operated group at all time points, which peaked at 8 hours (P<0.05). TUNEL staining showed that the apoptotic cells increased significantly in a time-dependent manner compared with the sham-operated group (P<0.01). Conclusions HI may lead to phosphorylation of STAT3 which probably induces the VEGF expression in the brain of neonatal rats. The activated STAT3 signaling pathway may be involved in the apoptosis regulation of nerve cells, and related to apoptosis inhibition of nerve cells.
信号转导和转录激活因子3 / 血管内皮生长因子 / 凋亡 / 缺氧缺血性脑损伤 / 新生大鼠
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 / Vascular endothelial growth factor / Apoptosis / Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage / Neonatal rats
国家教育部博士点基金(20120181120049);国家自然科学基金青年科学基金(81300526;81200462)。